3.2. 操作版本库
3.2.1. 强制推送
细心的读者可能从图3-4已经看出,显示的提交者并非gotgithub用户,而是一个名为ossxp-com的用户,这是因为GitHub是通过提交中的邮件地址来对应到GitHub用户的。看看提交说明:
$ git log --pretty=fullercommit 92dee9b8125afc9a606394ed463f9f264f2d3d58Author: Jiang XinAuthorDate: Wed Dec 14 14:52:40 2011 +0800Commit: Jiang XinCommitDate: Wed Dec 14 14:52:40 2011 +0800README for this project.
原来提交用户设置的邮件地址并非gotgithub用户设置的邮件地址。补救办法就是对此提交进行修改,然后强制推送到GitHub。
-
重新设置user.name和user.email配置变量。
因为gotgithub是一个仅在本书使用的示例账号,我可不想影响本地其他项目的提交,因此下面的设置命令没有使用--global参数,只对本地helloworld版本库进行设置。
$ git config user.name "Jiang Xin"$ git config user.email "gotgithub@gmail.com"
-
执行Git修补提交命令。
注意使用参数--reset-author会将提交信息中的属性Author连同AuthorDate一并修改,否则只修改Commit和CommitDate。参数-C HEAD维持提交说明不变。
$ git commit --amend --reset-author -C HEAD
- 查看提交日志,发现提交者信息和作者信息都已经更改。
$ git log --pretty=fullercommit e1e52d99fa71fd6f606903efa9da04fd0055fca9Author: Jiang XinAuthorDate: Wed Dec 14 15:05:47 2011 +0800Commit: Jiang XinCommitDate: Wed Dec 14 15:05:47 2011 +0800README for this project.
-
直接推送会报错。
错误信息中出现non-fast-forword(非快进式推送),含义为要推送的提交并非继远程版本库最新提交之后的提交,推送会造成覆盖导致服务器端有数据(提交)会丢失。
$ git pushTo git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.git! [rejected] master -> master (non-fast-forward)error: failed to push some refs to 'git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.git'To prevent you from losing history, non-fast-forward updates were rejectedMerge the remote changes (e.g. 'git pull') before pushing again. See the'Note about fast-forwards' section of 'git push --help' for details.
-
使用强制推送。
对于此例,考虑到还没有其他人关注helloworld这个刚刚建立的示例项目,显然不需要向上面命令的错误信息所提示的那样先执行git pull合并上游版本库再推送,而是选择强制推送,以新的修补提交覆盖包含错误提交者ID的提交。
$ git push -fCounting objects: 3, done.Delta compression using up to 2 threads.Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 629 bytes, done.Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)To git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.git+ 92dee9b...e1e52d9 master -> master (forced update)
完成强制推送后,再查看GitHub项目页面,会发现提交者已经显示为gotgithub用户。如图3-7所示。
图3-7:强制更新后,提交者已更改
3.2.2. 新建分支
Git的分支就是保存在.git/refs/heads/命名空间下的引用。引用文件的内容是该分支对应的提交ID。当前版本库中的默认分支master就对应于文件.git/refs/heads/master。
若在GitHub版本库中创建分支,首先要在本地版本库中创建新的分支(即引用),然后用推送命令将本地创建的新的引用连同所指向的提交推送到GitHub版本库中完成GitHub上分支的创建。操作如下:
-
本地版本库中建立新分支mybranch1。
创建分支有多种方法,如使用git branch命令,但最为便捷的就是git checkout-b命令,同时完成新分支的创建和分支切换。
$ git checkout -b mybranch1Switched to a new branch 'mybranch1'
- 为了易于识别,添加一个新文件hello1,并提交。
$ touch hello1$ git add hello1$ git commit -m "add hello1 for mark."[mybranch1 f46a284] add hello1 for mark.0 files changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)create mode 100644 hello1
- 通过推送命令,将本地分支mybranch1推送到GitHub远程版本库,完成在GitHub上的新分支创建。
$ git push -u origin mybranch1Counting objects: 4, done.Delta compression using up to 2 threads.Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 281 bytes, done.Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)To git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.git* [new branch] mybranch1 -> mybranch1Branch mybranch1 set up to track remote branch mybranch1 from origin.
在GitHub上查看版本库,会看到新增了一个分支mybranch1,不过默认分支仍为master,如图3-8所示。
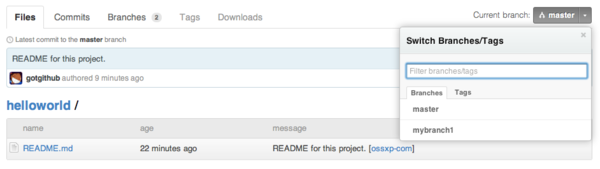
图3-8:版本库新增了一个分支
3.2.3. 设置默认分支
可以改变GitHub上版本库显示的默认分支,如果版本库包含多个分支的话。例如修改版本库的默认分支为mybranch1,点击项目名称旁边的“Admin”按钮,修改项目的默认分支。如图3-9所示。
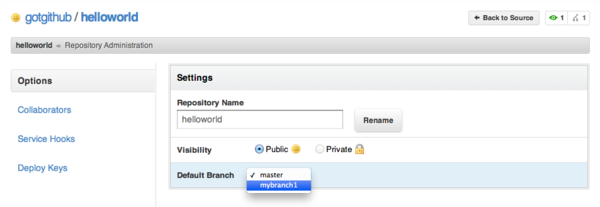
图3-9:设置缺省分支
设置了GitHub默认分支后,如果再从GitHub克隆版本库,本地克隆后版本库的默认分支也将改变。
$ git clone git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.git helloworld-nbCloning into 'helloworld-nb'...remote: Counting objects: 6, done.remote: Compressing objects: 100% (4/4), done.remote: Total 6 (delta 0), reused 6 (delta 0)Receiving objects: 100% (6/6), done.$ cd helloworld-nb$ git branch* mybranch1
实际上修改GitHub上版本库的默认分支,就是将GitHub版本库的头指针HEAD指向了其他分支,如mybranch1分支。这可以从下面命令看出。
$ git branch -rorigin/HEAD -> origin/mybranch1origin/masterorigin/mybranch1
也可以从git ls-remote命令看出头指针HEAD和引用refs/heads/mybranch1指向同一个对象的哈希值。
$ git ls-remoteFrom git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.gitf46a28484adb6c1b4830eb4df582325c740e9d6c HEADe1e52d99fa71fd6f606903efa9da04fd0055fca9 refs/heads/masterf46a28484adb6c1b4830eb4df582325c740e9d6c refs/heads/mybranch1
3.2.4. 删除分支
删除当前工作分支会报错。例如下面的命令试图分支mybranch1,但没有成功:
$ git branch -d mybranch1error: Cannot delete the branch 'mybranch1' which you are currently on.
错误信息显示不能删除当前工作分支。因此先切换到其他分支,例如从GitHub版本库中取出master分支并切换。
$ git checkout master
可以看出新的工作分支为master分支。
$ git branch* mastermybranch1
现在可以删除mybanch1分支。下面的命令之所以使用-D参数,而非-d参数,是因为Git在删除分支时为避免数据丢失,默认禁止删除尚未合并的分支。参数-D则可强制删除尚未合并的分支。
$ git branch -D mybranch1Deleted branch mybranch1 (was f46a284).
现在只是本地分支被删除了,远程GitHub服务器上的mybranch1分支尚在。删除远程GitHub版本库中的分支就不能使用git branch命令,而是要使用git push命令,不过在使用推送分支命令时要使用一个特殊的引用表达式(冒号前为空)。如下:
$ git push origin :mybranch1remote: error: refusing to delete the current branch: refs/heads/mybranch1To git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.git! [remote rejected] mybranch1 (deletion of the current branch prohibited)error: failed to push some refs to 'git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.git'
为什么删除远程分支出错了呢?是因为没有使用强制推送么?
实际上即使使用强制推送也会遇到上面的错误。GitHub发现要删除的mybranch1分支是远程版本库的缺省分支,因而禁止删除。重新访问GitHub的项目管理页面,将缺省分支设置回master分支,参照图3-9。然后再次执行如下命令,即可成功删除分支。
$ git push origin :mybranch1To git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.git- [deleted] mybranch1
执行git ls-remote命令可以看到GitHub远程版本库已经不存在分支mybranch1。
$ git ls-remote git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.gitFrom git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.gite1e52d99fa71fd6f606903efa9da04fd0055fca9 HEADe1e52d99fa71fd6f606903efa9da04fd0055fca9 refs/heads/master
3.2.5. 里程碑管理
里程碑即tag,其管理和分支管理非常类似。里程碑和分支一样也是以引用的形式存在的,保存在.git/refs/tags/路径下。引用可能指向一个提交,但也可能是其他类型(Tag对象)。
- 轻量级里程碑:用git tag [] 命令创建,引用直接指向一个提交对象。
- 带说明的里程碑:用git tag -a [] 命令创建,并且在创建时需要提供创建里程碑的说明。Git会创建一个tag对象保存里程碑说明、里程碑的指向、创建里程碑的用户等信息,里程碑引用指向该Tag对象。
- 带签名的里程碑:用git tag -s [] 命令创建。是在带说明的里程碑的基础上引入了PGP签名,保证了所创建的里程碑的完整性和不可拒绝性。
下面演示一下里程碑的创建和管理。
- 先在本地创建一个新提交。
$ touch hello1$ git add hello1$ git commit -m "add hello1 for mark."
- 本地创建里程碑mytag1、mytag2和mytag3。
$ git tag -m "Tag on initial commit" mytag1 HEAD^$ git tag -m "Tag on new commit" mytag2$ git tag mytag3
- 查看新建立的里程碑。
$ git tag -l -n1mytag1 Tag on initial commitmytag2 Tag on new commitmytag3 add hello1 for mark.
- 将本地里程碑推送到GitHub远程版本库。
$ git push origin refs/tags/*Counting objects: 6, done.Delta compression using up to 2 threads.Compressing objects: 100% (4/4), done.Writing objects: 100% (5/5), 548 bytes, done.Total 5 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)To git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.git* [new tag] mytag1 -> mytag1* [new tag] mytag2 -> mytag2* [new tag] mytag3 -> mytag3
- 删除本地里程碑。
$ git tag -d mytag3Deleted tag 'mytag3' (was c71231c)
- 删除GitHub远程版本库中的里程碑。
$ git push origin :mytag3To git@github.com:gotgithub/helloworld.git[deleted] mytag3
此时查看GitHub上的项目页,会看到已有两个里程碑,如图3-10所示。
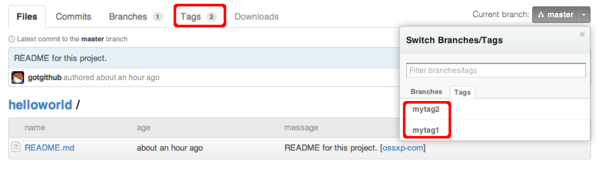
图3-10:里程碑列表