Hibernate的Session在事务级别进行持久化数据的缓存操作。
当然,也有可能分别为每个类(或集合),配置集群、或JVM级别(SessionFactory级别)的缓存。
你甚至可以为之插入一个集群的缓存。注意,缓存永远不知道其他应用程序对持久化仓库(数据库)可能进行的修改
(即使可以将缓存数据设定为定期失效)。
通过在hibernate.cache.provider_class属性中指定org.hibernate.cache.CacheProvider的某个实现的类名,你可以选择让Hibernate使用哪个缓存实现。Hibernate打包一些开源缓存实现,提供对它们的内置支持(见下表)。除此之外,你也可以实现你自己的实现,将它们插入到系统中。注意,在3.2版本之前,默认使用EhCache 作为缓存实现,但从3.2起就不再这样了。
表 19.1. 缓存策略提供商(Cache Providers)
| Cache | Provider class | Type | Cluster Safe | Query Cache Supported |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hashtable (not intended for production use) | org.hibernate.cache.HashtableCacheProvider |
memory | yes | |
| EHCache | org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider |
memory, disk | yes | |
| OSCache | org.hibernate.cache.OSCacheProvider |
memory, disk | yes | |
| SwarmCache | org.hibernate.cache.SwarmCacheProvider |
clustered (ip multicast) | yes (clustered invalidation) | |
| JBoss TreeCache | org.hibernate.cache.TreeCacheProvider |
clustered (ip multicast), transactional | yes (replication) | yes (clock sync req.) |
类或者集合映射的“<cache>元素”可以有下列形式:
<cache
usage="transactional|read-write|nonstrict-read-write|read-only"
region="RegionName"
include="all|non-lazy"
/>
 |
|
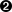 |
|
 |
|
另外(首选?), 你可以在hibernate.cfg.xml中指定<class-cache>和
<collection-cache> 元素。
这里的usage 属性指明了缓存并发策略(cache concurrency strategy)。
如果你的应用程序只需读取一个持久化类的实例,而无需对其修改,
那么就可以对其进行只读 缓存。这是最简单,也是实用性最好的方法。甚至在集群中,它也能完美地运作。
<class name="eg.Immutable" mutable="false">
<cache usage="read-only"/>
....
</class>
如果应用程序需要更新数据,那么使用读/写缓存 比较合适。
如果应用程序要求“序列化事务”的隔离级别(serializable transaction isolation level),那么就决不能使用这种缓存策略。
如果在JTA环境中使用缓存,你必须指定hibernate.transaction.manager_lookup_class属性的值,
通过它,Hibernate才能知道该应用程序中JTA的TransactionManager的具体策略。
在其它环境中,你必须保证在Session.close()、或Session.disconnect()调用前,
整个事务已经结束。 如果你想在集群环境中使用此策略,你必须保证底层的缓存实现支持锁定(locking)。Hibernate内置的缓存策略并不支持锁定功能。
<class name="eg.Cat" .... >
<cache usage="read-write"/>
....
<set name="kittens" ... >
<cache usage="read-write"/>
....
</set>
</class>
如果应用程序只偶尔需要更新数据(也就是说,两个事务同时更新同一记录的情况很不常见),也不需要十分严格的事务隔离,
那么比较适合使用非严格读/写缓存策略。如果在JTA环境中使用该策略,
你必须为其指定hibernate.transaction.manager_lookup_class属性的值,
在其它环境中,你必须保证在Session.close()、或Session.disconnect()调用前,
整个事务已经结束。
Hibernate的事务缓存策略提供了全事务的缓存支持,
例如对JBoss TreeCache的支持。这样的缓存只能用于JTA环境中,你必须指定
为其hibernate.transaction.manager_lookup_class属性。
没有一种缓存提供商能够支持上列的所有缓存并发策略。下表中列出了各种提供器、及其各自适用的并发策略。
表 19.2. 各种缓存提供商对缓存并发策略的支持情况(Cache Concurrency Strategy Support)
| Cache | read-only | nonstrict-read-write | read-write | transactional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hashtable (not intended for production use) | yes | yes | yes | |
| EHCache | yes | yes | yes | |
| OSCache | yes | yes | yes | |
| SwarmCache | yes | yes | ||
| JBoss TreeCache | yes | yes |